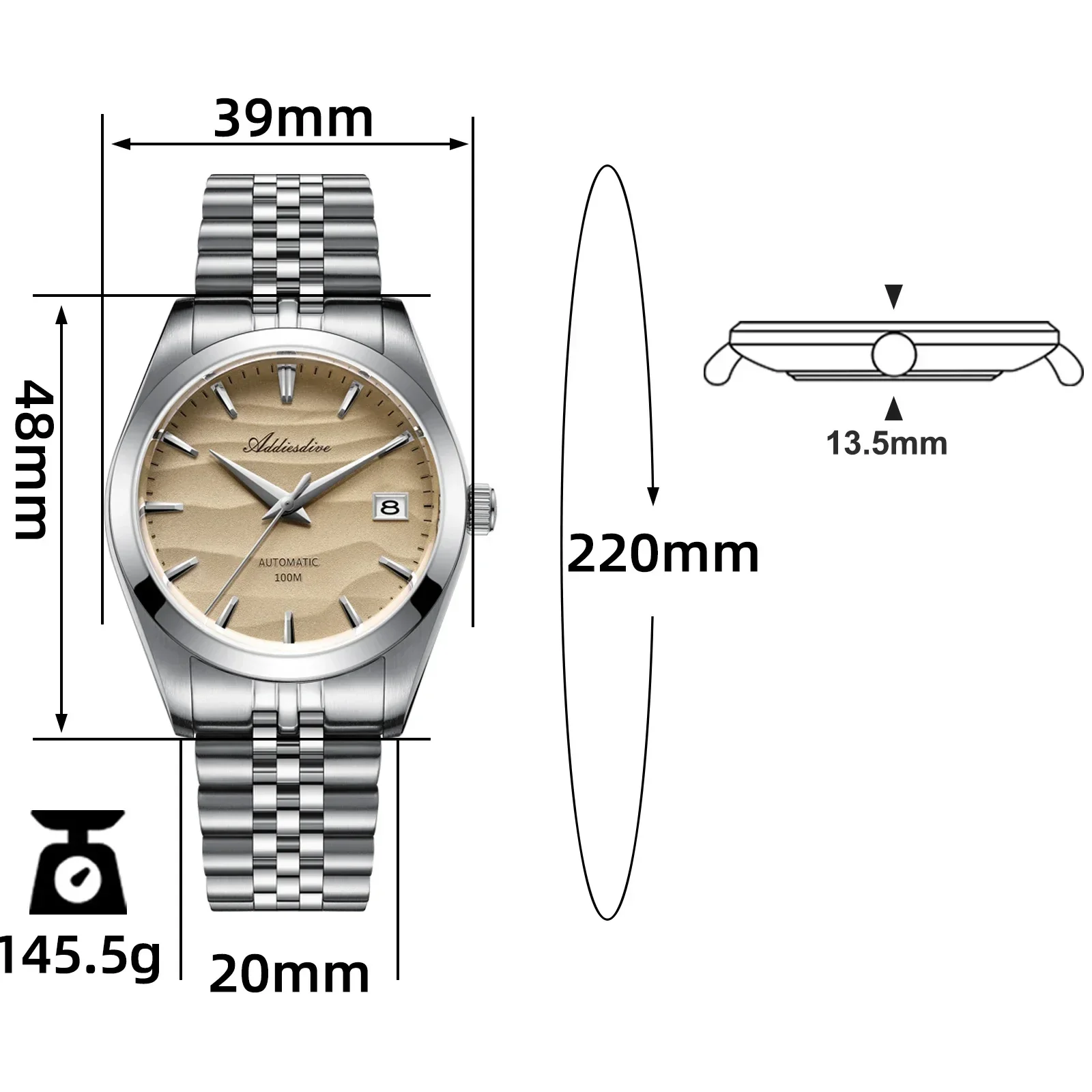
Introduction: The Perfect Balance of Comfort and Durability
Titanium has emerged as one of watchmaking’s most impressive materials, offering a combination of properties that seems almost contradictory. Watch enthusiasts and casual wearers alike are drawn to titanium timepieces for their feather-light feel on the wrist coupled with exceptional resilience against daily wear and tear.
This remarkable metal provides the perfect balance for watch wearers—delivering the comfort of a nearly weightless timepiece with the confidence that comes from wearing something built to last. While it might seem unusual for something so light to also be incredibly strong, the answer lies in titanium’s unique atomic structure and material properties.
Many prestigious watch manufacturers have embraced titanium for their high-performance models, particularly in sports and professional diving collections. The material’s growing popularity stems from the genuine functional advantages it offers, not merely as a marketing point.
Throughout historical dive watch engineering, titanium has revolutionized what we expect from a premium timepiece. Let’s explore the fascinating science behind why this metal delivers such an impressive combination of lightness and strength.
The Science of Titanium: Understanding the Material Properties
Titanium, identified as Element 22 on the periodic table, is a transition metal with properties that make it exceptionally valuable for high-performance applications. Despite being the ninth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, titanium wasn’t discovered until 1791 and wasn’t produced in pure form until the early 20th century.
What makes titanium truly special is its fundamental physical characteristics:
- Low density: At 4.5 g/cm³, titanium is approximately 45% lighter than stainless steel (which averages around 8 g/cm³)
- Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio: Provides comparable strength to steel at nearly half the weight
- Remarkable corrosion resistance: Forms a stable, protective oxide layer when exposed to oxygen
- Biocompatibility: Non-toxic and not rejected by human tissue, which explains its use in medical implants
These impressive properties stem from titanium’s atomic structure. The metal forms exceptionally strong bonds between atoms while maintaining a less dense crystalline structure than many other metals. This creates the seemingly contradictory combination of low weight and high strength.
The aerospace industry first recognized titanium’s potential, using it for critical aircraft components where weight savings were essential but strength couldn’t be compromised. The medical field followed, utilizing titanium for implants and surgical instruments. The watch industry eventually discovered that these same properties made titanium ideal for crafting exceptional timepieces.
Our titanium automatic watches collection showcases how these remarkable material properties translate into comfortable, durable timepieces for everyday wear.
Why Titanium Is Exceptionally Light: The Density Factor
To understand titanium’s lightness, we need to look at the concept of density—simply put, how much mass is packed into a given volume. Titanium’s atomic structure creates a metal that’s surprisingly light for its size.
When comparing common watch materials, the difference becomes clear:
- Titanium: 4.5 g/cm³
- Stainless Steel: 7.9-8.2 g/cm³
- 18K Gold: 15.5-19.3 g/cm³
- Platinum: 21.4 g/cm³
This means a titanium watch case weighs approximately 45% less than an identical stainless steel case. For a typical watch weighing 150 grams in steel, the titanium version might weigh just 80-85 grams—a difference immediately noticeable when worn.
This weight reduction comes from titanium’s atomic structure. Titanium atoms are arranged in what scientists call a hexagonal close-packed crystal structure. While the bonds between atoms are exceptionally strong, the overall arrangement is less dense than many other metals, particularly steel with its body-centered cubic structure.
In practical terms, this translates to a watch that doesn’t feel like it’s weighing down your wrist, even after hours of wear. The comfort difference is especially noticeable for larger watches or during active pursuits—a key reason why titanium has become popular for sports watches and why it’s prominently featured in the evolution of dive watch technology.
The Paradox of Strength: How Titanium Achieves Remarkable Durability
The truly fascinating aspect of titanium is how it maintains exceptional strength despite its lightweight nature. In material science, strength is measured in several ways:
- Tensile strength: Resistance to breaking under tension
- Yield strength: Ability to resist permanent deformation
- Hardness: Resistance to scratching or indentation
- Fatigue resistance: Ability to withstand repeated stress cycles
Titanium excels in most of these categories, particularly when its weight is factored in. The strength-to-weight ratio is where titanium truly shines—a critical factor in watchmaking where durability must be balanced with wearability.
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Density (g/cm³) | Strength-to-Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 5 Titanium | 895-1,000 | 4.43 | 202-226 |
| 316L Stainless Steel | 485-680 | 8.0 | 61-85 |
| Aluminum | 310 | 2.7 | 115 |
This exceptional strength comes from titanium’s strong interatomic bonds. When alloyed with small amounts of other elements like aluminum and vanadium (creating Grade 5 titanium, commonly used in high-performance watches), these properties are further enhanced.
Another remarkable property is titanium’s resistance to fatigue—the tendency of a material to weaken over time when subjected to repeated stress. This means a titanium watch case is less likely to develop structural weaknesses over years of daily wear, making it an excellent long-term investment.
For a comprehensive overview of these advantages along with potential drawbacks, our guide to titanium watches pros and cons provides in-depth analysis.
Titanium vs. Stainless Steel: The Ultimate Watch Material Comparison
When evaluating watch materials, titanium and stainless steel emerge as the two leading contenders. Each offers distinct advantages and limitations that affect the wearing experience, aesthetics, and longevity of a timepiece.
| Property | Titanium | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | 45% lighter | Heavier, more substantial feel |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | Strong but denser |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional (forms titanium dioxide) | Good (depends on grade) |
| Scratch Resistance | Lower (pure), Better with treatments | Generally better |
| Hypoallergenic | Excellent (biocompatible) | Contains nickel (potential allergen) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (doesn’t feel cold) | Higher (cold feeling in winter) |
| Appearance | Matte gray, subtle | Bright, high polish possible |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
The difference between titanium grades also matters significantly. Grade 2 titanium (commercially pure) is softer and more prone to scratching, while Grade 5 titanium (with 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium) offers superior hardness and scratch resistance.
Stainless steel watches typically use 316L steel, prized for its corrosion resistance and polishing capabilities. The higher density gives steel watches a substantial feel that some wearers prefer as it conveys a sense of quality and presence.
The aesthetic difference is also noteworthy—titanium typically has a more subdued, matte gray appearance compared to the bright, reflective finish possible with polished stainless steel. This subtle look has become increasingly popular for its understated elegance.
Our collection of rugged automatic watches includes both materials, allowing you to compare their distinct characteristics firsthand.
Titanium Watch Benefits: What It Means for Daily Wear
The technical properties of titanium translate into several tangible benefits for watch wearers:
All-day comfort: The reduced weight means less fatigue during extended wear, making titanium watches ideal for those who wear timepieces throughout long workdays.
Perfect for active lifestyles: Athletes and outdoor enthusiasts appreciate how a lighter watch interferes less with movement and activity while maintaining durability.
Hypoallergenic properties: Unlike stainless steel, which contains nickel that can cause skin irritation for sensitive individuals, titanium is biocompatible and rarely causes allergic reactions.
Temperature neutral: Titanium has lower thermal conductivity than steel, meaning it doesn’t feel as cold against the skin in winter months and warms to body temperature more quickly.
Corrosion resistance in harsh environments: Particularly valuable for dive watches or timepieces exposed to saltwater, sweat, or chemicals, titanium resists deterioration in conditions that would challenge other materials.
Long-term durability: The combination of corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance means titanium watches often maintain their structural integrity longer than alternatives.
These practical benefits explain why titanium is used in watches across various price points, from affordable sports models to high-end luxury timepieces. The material choice isn’t merely about technical specifications—it fundamentally changes how a watch feels and performs in real-world situations.
The Corrosion Resistance Advantage: Why Titanium Watches Last
One of titanium’s most remarkable properties is its exceptional resistance to corrosion. When exposed to oxygen, titanium instantly forms a protective layer of titanium dioxide on its surface. This naturally occurring oxide film is just 10-20 nanometers thick but provides remarkable protection against chemical attack.
This self-forming barrier gives titanium several advantages:
Resistance to saltwater: Crucial for dive watches, titanium remains virtually unaffected by prolonged exposure to seawater that would corrode many other metals.
Sweat resistance: The acidic nature of human perspiration doesn’t degrade titanium, making it ideal for sports watches and daily wear.
Self-healing properties: If the oxide layer is scratched or damaged, it immediately reforms when exposed to oxygen, providing continuous protection.
No tarnishing or discoloration: Unlike silver or some stainless steels, titanium maintains its appearance without developing patina or oxidation stains.
This corrosion resistance is a key reason why titanium has featured prominently in the timeline of diving watch innovations. Early diving watches faced significant challenges with water ingress and corrosion, problems that titanium helped solve with its natural properties.
For watch owners, this translates to lower maintenance requirements and confidence that their timepiece will maintain its structural integrity and appearance for decades, even with frequent exposure to challenging environments.
Surface Treatments: Enhancing Titanium’s Natural Properties
While titanium offers impressive strength and corrosion resistance, its surface hardness in pure form is actually lower than that of hardened stainless steel. This makes untreated titanium more susceptible to scratches and surface marks—a potential drawback for watch cases.
To address this vulnerability, watch manufacturers employ various treatments to enhance titanium’s surface hardness:
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating: Creates an extremely hard, scratch-resistant black layer with excellent friction properties
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Bonds various compounds to titanium for increased hardness and distinctive colorations
Proprietary hardening processes: Many brands have developed unique surface treatments, such as Citizen’s “Super Titanium” which is five times more scratch-resistant than standard titanium
Cold working and heat treatments: Mechanical and thermal processes that increase hardness without coatings
Titanium carbide layer formation: Creates an extremely hard surface layer integrated with the base metal
These treatments can increase surface hardness dramatically, sometimes exceeding that of hardened steel, while maintaining titanium’s lightweight properties and corrosion resistance.

Another interesting property of titanium is its excellent heat resistance in watch cases, which allows for these advanced treatments without compromising structural integrity.
Different Titanium Alloys and Grades in Watchmaking
Not all titanium watches are created equal. The specific grade and alloy composition significantly impact a watch’s properties and performance characteristics.
The most common titanium varieties in watchmaking include:
| Grade | Composition | Properties | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 2 | Commercially pure (99.2%) | Excellent corrosion resistance, moderate strength, more scratch-prone | Entry to mid-level watches |
| Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | 90% Ti, 6% Al, 4% V | Higher strength, better scratch resistance, harder to machine | Luxury and professional watches |
| Beta titanium | Various beta-phase alloys | Higher strength, better cold workability | High-end cases and bracelets |
| Proprietary alloys | Brand-specific formulations | Enhanced properties for specific applications | Premium luxury watches |
Grade 5 titanium is generally considered superior for watch cases due to its enhanced strength and scratch resistance. However, it’s more difficult and expensive to machine, which contributes to the higher cost of watches using this material.
Some high-end manufacturers have developed their own proprietary titanium alloys or composite materials that combine titanium with other elements for specific performance characteristics. These innovations continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with titanium watchmaking.
Our professional spec dive watches collection features various titanium grades, each selected for optimal performance in challenging underwater environments.
Potential Drawbacks: What to Consider Before Choosing Titanium
While titanium offers impressive benefits for watch construction, it’s important to consider potential limitations before making a purchase:
Higher cost: Manufacturing processes for titanium are more complex and energy-intensive than for stainless steel, resulting in higher prices for comparable designs.
Scratch visibility: Despite treatments, many titanium watches still show scratches more readily than hardened steel. The lighter color and matte finish can make surface marks more noticeable.
Difficult repairs: Titanium is challenging to polish and repair once damaged. Specialized equipment and expertise are required, which can make servicing more expensive and complicated.
Aesthetic considerations: The distinctive matte gray appearance of titanium cannot achieve the same high-polish, reflective finish that many appreciate in steel or precious metal watches.
Subjective weight perception: Some watch enthusiasts actually prefer the substantial heft of steel or gold, associating weight with quality and luxury.
Limited color options: While treatments can create black or colored titanium, the range of finishes is more limited compared to other materials.
Understanding these tradeoffs helps set realistic expectations for titanium watches. For many users, the comfort and durability advantages far outweigh these considerations, particularly for watches designed for rugged conditions and extreme environments.
Is a Titanium Watch Right for You? Making the Right Choice
Deciding whether titanium is the right material for your next watch depends on your specific priorities and wearing habits:
Who benefits most from titanium watches?
Titanium is ideal if you prioritize comfort, especially for all-day wear or larger watch cases. Athletes, outdoor enthusiasts, and those with active lifestyles will appreciate the reduced weight during movement. People with sensitive skin or metal allergies will benefit from titanium’s hypoallergenic properties.
When might steel be preferable?
If you prefer the substantial feel of a heavier watch or favor high-polish, reflective finishes, stainless steel might better suit your taste. Those who are particularly concerned about visible scratches might also prefer hardened stainless steel.
Which watch styles benefit most from titanium construction?
Dive watches, sports watches, and tool watches gain significant functional advantages from titanium construction. The weight savings are most noticeable in larger case sizes (42mm and above), making titanium an excellent choice for these bolder designs.

For those seeking the perfect balance of lightweight comfort and rugged durability, our automatic field and military watches collection offers excellent titanium options.
Military Inspired Automatic Watches, Rugged Automatic Watches, Tactical Automatic Watches
Price range: $852.14 through $994.60 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageBronze Automatic Watches, Military Inspired Automatic Watches, Professional Spec Dive Watches
Price range: $1,442.21 through $1,442.82 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageProfessional Spec Dive Watches, Titanium Automatic Watches
$574.74 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageClassic Pilot Watches, Military Inspired Automatic Watches
$561.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageRugged Automatic Watches, Unique Automatic Watches
Price range: $228.96 through $231.10 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageClassic Field Watches, Military Inspired Automatic Watches
Price range: $280.87 through $338.51 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Frequently Asked Questions About Titanium Watches
Are titanium watches completely scratch-proof?
No, titanium watches are not scratch-proof. Untreated titanium is actually more prone to surface scratches than hardened stainless steel. However, many modern titanium watches use surface treatments like DLC coating or proprietary hardening processes that significantly improve scratch resistance.
How much lighter is a titanium watch compared to stainless steel?
A titanium watch typically weighs about 45% less than an identical stainless steel model. For example, a 150-gram stainless steel watch would weigh approximately 80-85 grams in titanium.
Can titanium watches be repaired if damaged?
Yes, but repairs are more challenging than with stainless steel. Titanium requires specialized tools and expertise to weld, reshape, or refinish. Finding watchmakers skilled in titanium repair may be more difficult, and the services often cost more.
Do titanium watches tarnish or change color over time?
No, titanium is highly resistant to tarnishing and discoloration. The stable oxide layer that forms on its surface prevents further oxidation, allowing titanium watches to maintain their appearance for decades without the patina that develops on some other metals.
Are titanium watches worth the premium price?
For those who value lightweight comfort, corrosion resistance, and hypoallergenic properties, the premium is often justified. The value proposition is strongest for watches intended for daily wear, active lifestyles, or exposure to harsh environments like saltwater.
How do I properly care for a titanium watch?
Rinse with fresh water after exposure to saltwater or chemicals. Clean occasionally with mild soap and water using a soft brush for bracelet links. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage surface treatments. While titanium is durable, it’s still best to avoid unnecessary impacts that could cause dents or scratches.
For more information on maintaining your timepiece for decades of reliable service, see our guide on how long automatic watches last.
The Future of Titanium in Luxury Watchmaking
The watchmaking industry continues to innovate with titanium, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with this remarkable metal:
Advanced metallurgical techniques are creating new titanium alloys with enhanced properties—greater hardness, improved machinability, and even more refined aesthetics. Some manufacturers are developing multi-layer composites that combine titanium’s lightweight properties with other materials’ advantages.
We’re also seeing more sophisticated surface treatments that significantly improve scratch resistance while maintaining titanium’s natural lightweight properties. These innovations address one of the primary historical concerns about titanium watches.
Another exciting trend is the combination of titanium with other cutting-edge materials like ceramic, carbon fiber, and advanced polymers. These hybrid approaches take advantage of each material’s strengths while minimizing limitations.
As consumers increasingly prioritize comfort and wearability alongside durability, titanium’s position in luxury watchmaking seems assured. The material’s unique combination of properties continues to make it the perfect choice for those who want their timepiece to be both a pleasure to wear and built to last.







